In today's data-driven world, having access to a vast amount of information is a competitive advantage. Whether you're a data scientist, business analyst, or just curious about a particular topic, web scraping is a powerful technique that can help you collect and analyze data from the internet. In this blog post, we'll explore what web scraping is, how it works, and how you can get started with it.
What is Web Scraping?
Web scraping, also known as web harvesting or web data extraction, is the process of automatically extracting information from websites. It involves fetching web pages, parsing HTML or other structured data, and then extracting specific data elements for further analysis or storage. This technique allows you to turn unstructured web data into structured and actionable information.

Why Web Scraping?
There are several reasons why web scraping is a valuable skill:
Data Collection: Web scraping allows you to collect data from websites that don't offer APIs or downloadable datasets.
Real-time Information: You can access and update data in real-time, making it ideal for tracking stock prices, weather updates, news headlines, and more.
Competitive Analysis: Businesses can use web scraping to monitor competitors' prices, product listings, and customer reviews.
Research: Researchers and academics can gather data for studies and analysis.
How Does Web Scraping Work?
Web scraping typically involves the following steps:
Sending HTTP Requests: The process starts with sending HTTP requests to the target website's server. This request fetches the web page's HTML content.
HTML Parsing: Once the HTML content is retrieved, you'll need to parse it. Libraries like BeautifulSoup (Python) or Cheerio (Node.js) help parse the HTML and extract relevant data.
Data Extraction: After parsing, you can extract specific data elements such as text, images, links, or tables based on your requirements.
Data Storage: Depending on your project, you can store the extracted data in various formats like CSV, JSON, or databases.
Getting Started with Web Scraping
If you're interested in trying web scraping, here's a simplified example using Python and BeautifulSoup.
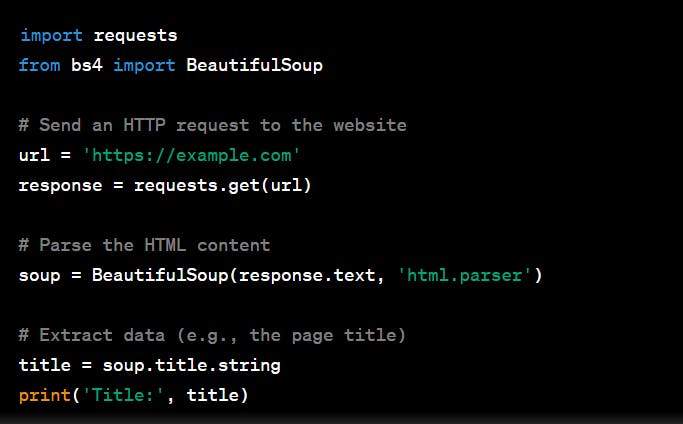
This code sends a request to 'example.com,' parses the HTML, and extracts the page title. Of course, web scraping can be much more complex depending on the target website and the data you want to collect.
Legal and Ethical Considerations

Before you dive into web scraping, it's crucial to be aware of legal and ethical considerations. Always check a website's robots.txt file for scraping guidelines, respect the website's terms of service, and avoid overloading their servers with too many requests.
Conclusion
Web scraping is a powerful technique that empowers individuals and businesses to gather valuable data from the web. It offers endless possibilities for research, analysis, and decision-making. However, it's essential to approach web scraping responsibly and ethically. As you explore this field, you'll discover countless opportunities to leverage web data for various purposes.
If you're interested in diving deeper into web scraping, there are numerous online tutorials, courses, and libraries available to help you on your journey. Happy scraping!