What are machine learning and its life cycle about? You’ll get different answers from different people.
Programmers might say that it’s about programming with Python and sophisticated mathematical algorithms.
Business stakeholders usually associate machine learning with data, and a dash of mystery.
Machine learning engineers tend to talk about model training and data wrangling.
So who is right? Everyone.
Machine learning is about data – no lie there. There’s no machine learning without a decent amount of data for the machine to learn from. The amount of available data is growing exponentially, which makes machine learning development easier than ever.
The connection between machine learning and algorithms is also on point. Indeed, there are complex mathematical methods that force machines to learn. No math – no machine learning.
Lastly, model training and data preparation is indeed the core of every ML project. Machine learning engineers spend a substantial amount of time training models and preparing datasets. That’s why it’s the first thing ML engineers think of.
Machine learning is about development, manipulating data, and modeling. All of these separate parts together form a machine learning project life cycle, and that’s exactly what we’re going to talk about in this article.
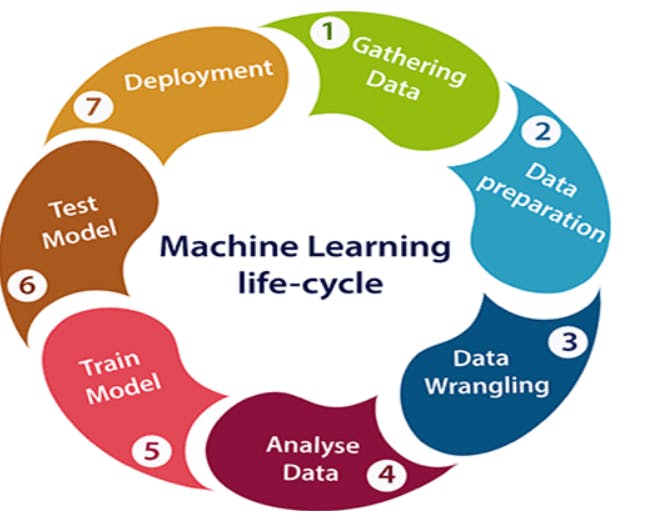
The Machine learning life cycle involves seven major steps, which are given below:
Gathering Data
Data preparation
Data Wrangling
Analyse Data
Train the model
Test the model
Deployment
1. GATHERING DATA
Data Gathering is the first step of the machine learning life cycle. The goal of this step is to identify and obtain all data-related problems.
In this step, we need to identify the different data sources, as data can be collected from various sources such as files, databases, the internet, or mobile devices. It is one of the most important steps of the life cycle. The quantity and quality of the collected data will determine the efficiency of the output. The more will be the data, the more accurate will be the prediction.

2. DATA PREPARATION
After collecting the data, we need to prepare it for further steps. Data preparation is a step where we put our data into a suitable place and prepare it to use in our machine learning training.
In this step, first, we put all data together, and then randomize the ordering of data.
This step can be further divided into two processes:
Data exploration:
It is used to understand the nature of the data that we have to work with. We need to understand the characteristics, format, and quality of data.
A better understanding of data leads to an effective outcome. In this, we find Correlations, general trends, and outliers.Data pre-processing:
Now the next step is preprocessing of data for its analysis.
3. DATA WRANGLING
Data wrangling is the process of cleaning and converting raw data into a usable format. It is the process of cleaning the data, selecting the variable to use, and transforming the data into a proper format to make it more suitable for analysis in the next step. It is one of the most important steps of the complete process. Cleaning of data is required to address the quality issues.
The data we have collected don't need to be always for our use as some of the data may not be useful. In real-world applications, collected data may have various issues, including:
Missing Values
Duplicate data
Invalid data
Noise
So, we use various filtering techniques to clean the data.

4. DATA ANALYSIS
Now the cleaned and prepared data is passed on to the analysis step. This step involves:
Selection of analytical techniques
Building models
Review the result
This step aims to build a machine-learning model to analyze the data using various analytical techniques and review the outcome. It starts with the determination of the type of the problems, where we select the machine learning techniques such as Classification, Regression, Cluster analysis, Association, etc. then build the model using prepared data, and evaluate the model.
Hence, in this step, we take the data and use machine learning algorithms to build the model.
5. TRAIN MODEL
Now the next step is to train the model, in this step, we train our model to improve its performance for a better outcome of the problem.
We use datasets to train the model using various machine-learning algorithms. Training a model is required so that it can understand the various patterns, rules, and, features.
6. TEST MODEL
Once our machine learning model has been trained on a given dataset, then we test the model. In this step, we check for the accuracy of our model by providing a test dataset to it.
Testing the model determines the percentage accuracy of the model as per the requirement of the problem.
7. DEPLOYMENT
The last step of the machine learning life cycle is deployment, where we deploy the model in a real-world system.
If the above-prepared model is producing an accurate result as per our requirement with acceptable speed, then we deploy the model in the real system. But before deploying the project, we will check whether it is improving its performance using available data or not. The deployment phase is similar to making the final report for a project.
